Spring 2016 Geography C135 Final Project
Eastern Route Project
Eastern route project began construction in 2002. It will divert water from the lower reach of the Yangtze River north to eastern Huang-Huai-Hai Plain with the termination in Tianjin by raising water in stages though the Grand Canal (SNWT official website).
The total length of the main canal would be about 1150 km. When it is completed, the eastern route is expected to deliver 14.8 billion m3 of Yangtze water to northern China. However, according to Magee, one big challenge which complicates the project is gravity. He points out that the Grand Canal’s channel bed elevation above sea level gradually increases over the first (southern) two-thirds of the total length, rising about 130 feet (40 m) from Hangzhou to Jining in Shandong Province where it reaches its maximum elevation. Thus, eastern route project has already developed a water conveyance system which includes the main diversion channel, pumping station and Yellow River-crossing project.
For the diversion channel, the Grand Canal will be the trunk diversion channel and some other subsidiary diversion routes will be added to partial diversion channel sections.
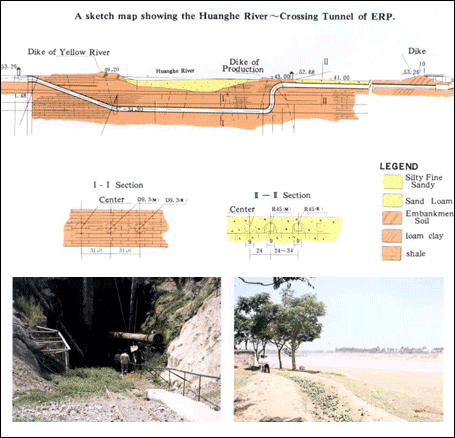
For pumping stations, since the topography along Yellow River is of the higher center. The diversion spot will be lower than the surface near Yellow River by 36-37 m. There are 13 pumping stations to pump water from the Yangtze River to the southern bank of Yellow River with the total lifting height of 65 m. As the official website of the project shows that the characteristics of the pumping station will include low lifting height (2-6 m), large flow (15-40 m3/s for each unit), long operating time (5000 hours/year for the stations in the south of Yellow River). In addition to the main division channel and pumping stations, the project also requires tunneling under Yellow River. The tunneling solves the problem of leakage control for excavation under the riverbed.